课前
BEFORE CLASS
课前测评,了解情况,获取针对性学习计划
领取内部学习资料、了解课程安排以及服务内容
领取学习、复习计划,完成开课前内容学习
课中
IN THE CLASS
实时反馈学习结果,及时调整学习、复习计划
及时完成课后学习内容、以及课上知识点复习
学习问题反馈,及时给到老师在课上予以解答
课后
AFTER CLASS
根据同学学习情况,提供课后学习计划、冲刺学习计划等
保障课后服务执行到位(答疑服务、课程回放、后续课程、报名指导等)
考试后免费分析成绩和提供专业的针对性提升方案
双系统教学体系
三重保障 为700+保驾护航
五阶段全程陪伴
科学的课程设计,10年教学经验积累,实力研发针对GMAT考试规则的课程体系
核心方法
数学4大考点,27个知识点;SC8大考点,
7种核心关系,CR5大推理模型8大题型;
RC6种阅读关系3大类考点。
解决突破
方法灵活应用,轻松应对各类考点的高阶
难题。
核心方法课
针对GMAT考试分项,搭建解题框架,
逐一击破考点。
解决突破课
针对各种考点变化,构造解题思路,
灵活应对各类高阶难题。

硬核资深讲师团队+全班型覆盖
资深教师阵容,每一位老师都有丰富的教学、授课经验。 课程选择丰富,适合自己的才是最好的。
GMAT资料合集;执行保障300难题/OG中文解析;1对1学管老师;私人订制学习计划; 学习进度分析报告;考前机经课;资深讲师解答; 学习社群;刷题/单词APP;仿真模考系统; 换库日历;考位查询小程序。
科学课程体系,整体提升出分效率。 紧跟GMAT考点,构建解题思维,课前课中课后三阶段全程聚焦学习进度。
1对1个性化复习方案,每周定期跟进,动态调整复习节奏
每日学习计划
每周两次跟进
动态调整复习节奏
全程监督辅导
1v1个性化复习方案
 申友雷哥GMAT高分时刻
申友雷哥GMAT高分时刻
学生评语

王同学
强烈推荐Verna老师的SC直播课和Amanda老师的SC录播课,两个全都看完有种打通任督二脉的感觉,老师们商科的时候细节扣的很细
孙同学
我好喜欢Cheryl老师啊,每节课的内容都能直击痛点,让我的CR有种醍醐灌顶的感觉,真的推翻了我之前的自学方法,效果特别好
黄同学
elisha老师的课我爱了,感觉每一句话都是重点,他讲东西我就是很愿意听,而且不会走神想其他的
陆同学
Verna老师上课互动特别多,打call!,上她的课能让我在课上就发现思路问题并及时纠正,细节扣得很细
张同学
Kevin和amanda老师的课不愧是申友王牌,就上了六节1对1让我出分740,真的是GMAT提分的一剂猛药
杨同学
首先amanda老师俺女神,让我SC有了思路,做题也轻松不少。我觉得语文还是不在于刷题在于思路!数学的话也要先熟悉考点和知识点再刷题 申友雷哥GMAT讲师
申友雷哥GMAT讲师
 申友雷哥GMAT备考宝典
申友雷哥GMAT备考宝典
 申友雷哥GMAT面授地址
申友雷哥GMAT面授地址
MAT+旨在更好的服务于用户帮助学生能够快速上分,现已在上海、北京、广州、成都、武汉等地开设分公司
考生可以更好的于GMAT+面对面互动学习

上海申友教室
上海市徐汇区文定路208号德必徐家汇WE艺术楼2楼205
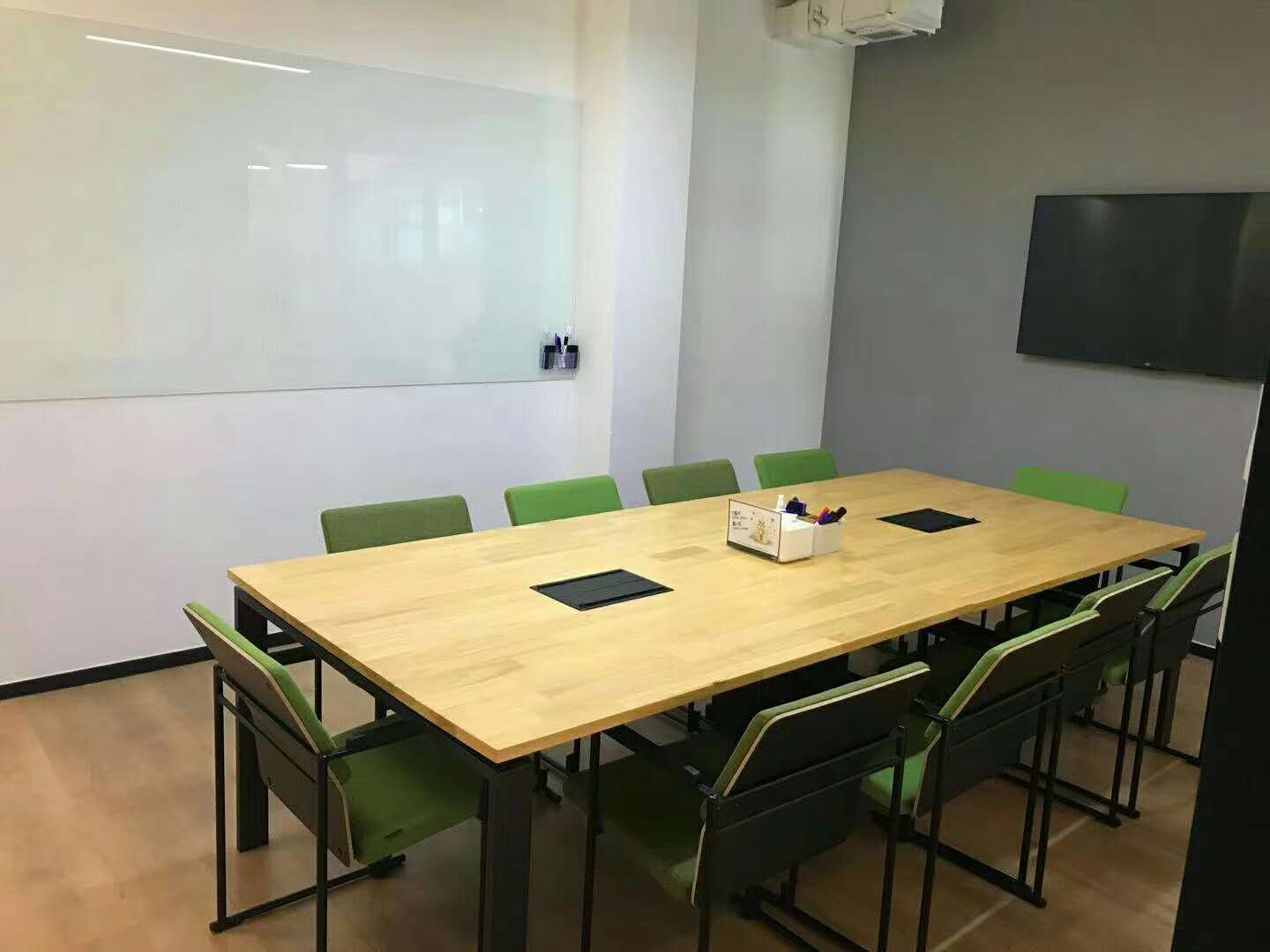

北京申友教室
北京市朝阳区雅宝路7号 E园EPARK大厦504

长沙申友教室
湖南省长沙市开福区万达广场-C3 1510室
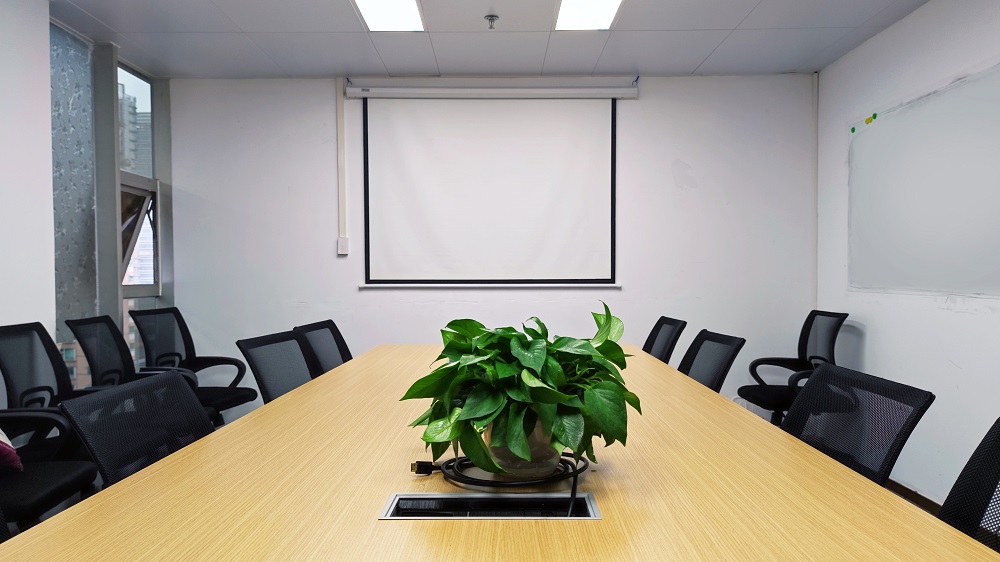

广州申友教室
广州市天河区体育东路116号财富广场西塔1206
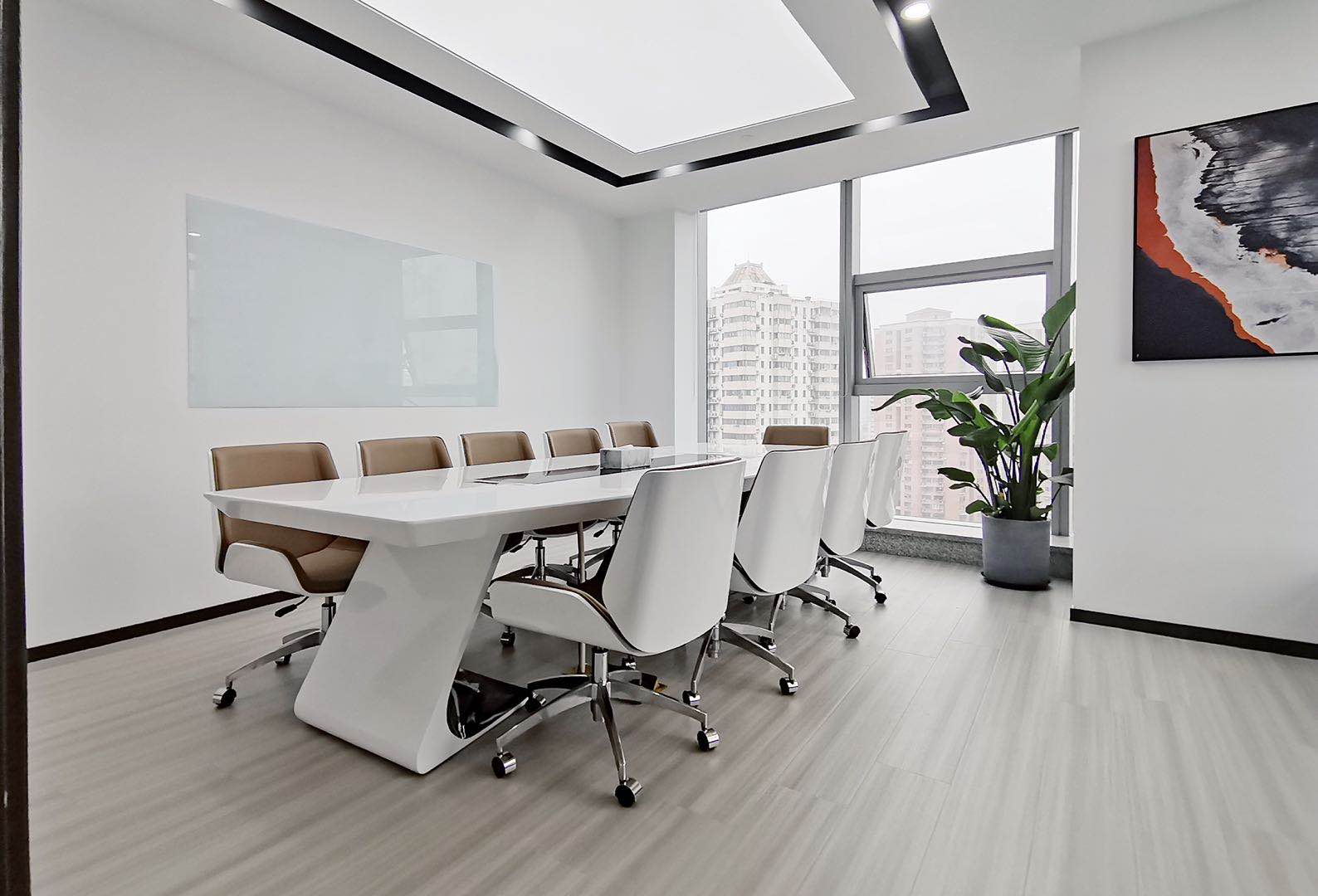

重庆申友教室
重庆市渝中区邹容路68号大都会广场16楼1603-1604室

青岛申友教室
青岛市南区香港中路36号招银大厦1006
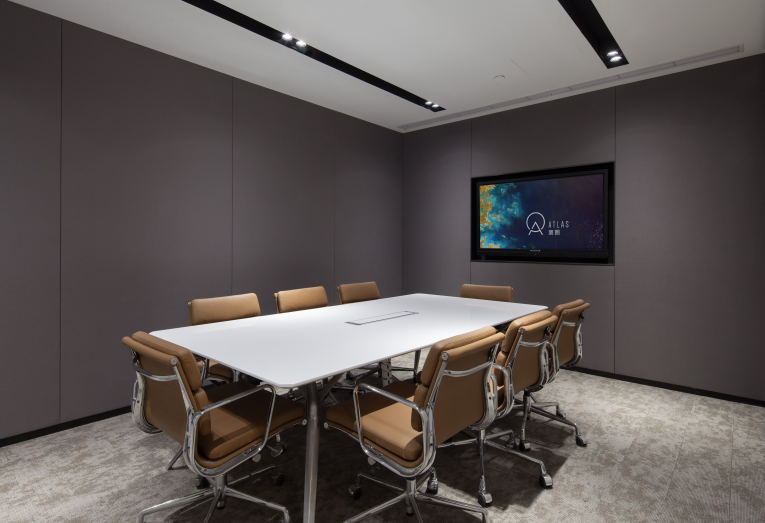

成都申友教室
四川省成都市锦江区春熙路街道梓潼桥正街25号西部文化产业中心7-8楼
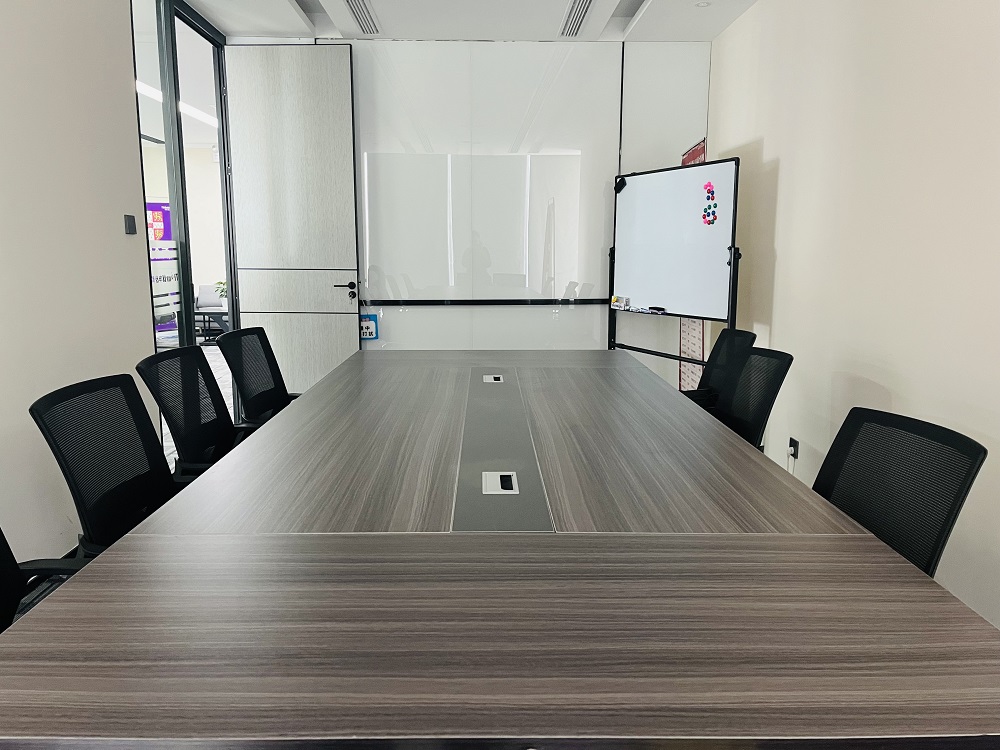

武汉申友教室
湖北省武汉市洪山区珞喻路889号光谷融众国际23层2302室
 申友雷哥GMAT高分教材
申友雷哥GMAT高分教材

申友GMAT长难句之光

GMAT阅读高分攻略

申友GMAT语法真题名师解析

申友GMAT700+系列阅读紫皮书

申友GMAT第九代教材,CR+Q+IR部分

申友GMAT第九代高分教材,AWA+RC部分









 请填写手机号
请填写手机号
关闭

Copyright © 2021 All Right Reserved 申友雷哥教育 版权所有 沪ICP备17005516号-3 免责声明 互联网经营许可证编号:沪B2-20210282